Git integration (GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket)
Your Read the Docs account can be connected to your Git provider’s account. Connecting your account provides the following features:
- 🔑️ Easy login
Log in to Read the Docs with your GitHub, Bitbucket, or GitLab account.
- 🔁️ List your projects
Select a project to automatically import from all your Git repositories and organizations. See: Adding a documentation project.
- ⚙️ Automatic configuration
Have your Git repository automatically configured with your Read the Docs webhook, which allows Read the Docs to build your docs on every change to your repository.
- 🚥️ Commit status
See your documentation build status as a commit status indicator on pull request builds.
See also
- Manually add your project
Using a different provider? You can configure it manually. Read the Docs still supports other providers such as Gitea or GitHub Enterprise.
Getting started
- ✅️ Signed up with your Git provider?
If you signed up or logged in to Read the Docs with your GitHub, Bitbucket, or GitLab credentials, you’re all done. Your account is connected.
The rest of this guide explains how the automatic configuration works.
- ⏩️️ Signed up with your email address?
If you have signed up to Read the Docs with your email address, you can add the connection to the Git provider afterward. You can also add a connection to an additional Git provider this way.
Please follow How to connect your Read the Docs account to your Git provider in this case.
Once you have your account connected, you can follow the Adding a documentation project guide to actually add your project to Read the Docs.
How automatic configuration works
When your Read the Docs account is connected to GitHub, Bitbucket, or GitLab and you add a new Read the Docs project:
Read the Docs automatically creates a Read the Docs Integration that matches your Git provider.
Read the Docs creates an incoming webhook with your Git provider, which is automatically added to your Git repository’s settings using the account connection.
After project creation, you can continue to configure the project. All settings can be modified, including the ones that were automatically created.
Tip
A single Read the Docs account can connect to many different Git providers. This allows you to have a single login for all your various identities.
Read the Docs incoming webhook
Accounts with GitHub, Bitbucket, and GitLab integration automatically have Read the Docs’ incoming webhook configured on all Git repositories that are imported. Other setups can set up the webhook through manual configuration.
When an incoming webhook notification is received, Read the Docs ensures that it matches an existing project. Once the webhook is validated, an action is taken based on the information inside of the webhook.
Possible webhook action outcomes are:
Builds the latest commit.
Synchronizes your versions based on the latest tag and branch data in Git.
Creates a pull request build.
Runs your automation rules.
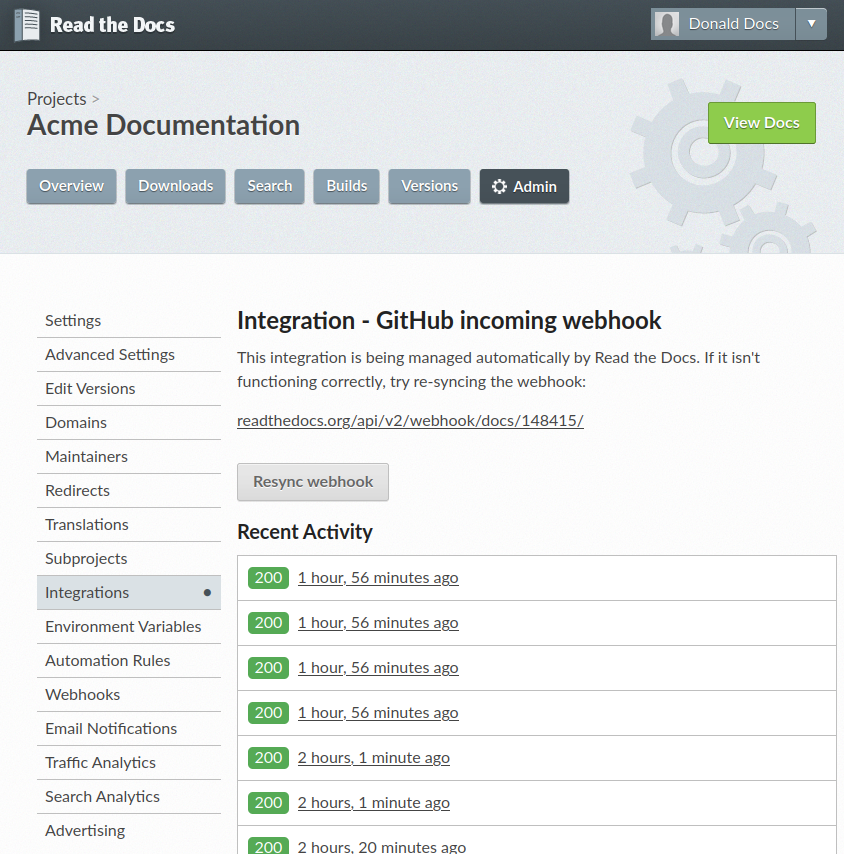
All calls to the incoming webhook are logged. Each call can trigger builds and version synchronization.
On Read the Docs for Business, Git integration makes it possible for us to synchronize your Git repository’s access rights from your Git provider. That way, the same access rights are effective on Read the Docs and you don’t have to configure access in two places. See more in our Single sign-on with GitHub, Bitbucket, or GitLab.
How does the connection work?
Read the Docs uses OAuth to connect to your account at GitHub, Bitbucket, or GitLab. You are asked to grant permissions for Read the Docs to perform a number of actions on your behalf.
At the same time, we use this process for authentication (login) since we trust that GitHub, Bitbucket, or GitLab have verified your user account and email address.
By granting Read the Docs the requested permissions, we are issued a secret OAuth token from your Git provider. Using the secret token, we can automatically configure repositories during project creation. We also use the token to send back build statuses and preview URLs for pull requests.
Note
Access granted to Read the Docs can always be revoked. This is a function offered by all Git providers.
Git provider integrations
If your project is using Organizations (Read the Docs for Business) or maintainers (Read the Docs Community), then you need to be aware of who is setting up the integration for the project.
The Read the Docs user who sets up the project through the automatic import should also have admin rights to the Git repository.
A Git provider integration is active through the authentication of the user that creates the integration. If this user is removed, make sure to verify and potentially recreate all Git integrations for the project.
Permissions for connected accounts
Read the Docs does not generally ask for write permission to your repository code (with one exception detailed below). However, we do need permissions for authorizing your account so that you can log in to Read the Docs with your connected account credentials.
Read the Docs requests the following permissions (more precisely, OAuth scopes) when connecting your Read the Docs account to GitHub.
- Read access to your email address (
user:email) We ask for this so you can create a Read the Docs account and log in with your GitHub credentials.
- Administering webhooks (
admin:repo_hook) We ask for this so we can create webhooks on your repositories when you import them into Read the Docs. This allows us to build the docs when you push new commits.
- Read access to your organizations (
read:org) We ask for this so we know which organizations you have access to. This allows you to filter repositories by organization when importing repositories.
- Repository status (
repo:status) Repository statuses allow Read the Docs to report the status (e.g. passed, failed, pending) of pull requests to GitHub.
Note
Read the Docs for Business
asks for one additional permission (repo) to allow access to private repositories
and to allow us to set up SSH keys to clone your private repositories.
Unfortunately, this is the permission for read/write control of the repository
but there isn’t a more granular permission
that only allows setting up SSH keys for read access.
We request permissions for:
- Administering your repositories (
repository:admin) We ask for this so we can create webhooks on your repositories when you import them into Read the Docs. This allows us to build the docs when you push new commits. NB! This permission scope does not include any write access to code.
- Reading your account information including your email address
We ask for this so you can create a Read the Docs account and log in with your Bitbucket credentials.
- Read access to your team memberships
We ask for this so we know which organizations you have access to. This allows you to filter repositories by organization when importing repositories.
- Read access to your repositories
We ask for this so we know which repositories you have access to.
To read more about Bitbucket permissions, see official Bitbucket documentation on API scopes
Like the others, we request permissions for:
Reading your account information (
read_user)API access (
api) which is needed to create webhooks in GitLab
GitHub permission troubleshooting
Repositories not in your list to import.
Many organizations require approval for each OAuth application that is used, or you might have disabled it in the past for your personal account. This can happen at the personal or organization level, depending on where the project you are trying to access has permissions from.
You need to make sure that you have granted access to the Read the Docs OAuth App to your personal GitHub account. If you do not see Read the Docs in the OAuth App settings, you might need to disconnect and reconnect the GitHub service.
See also
GitHub docs on requesting access to your personal OAuth for step-by-step instructions.
You need to make sure that you have granted access to the Read the Docs OAuth App to your organization GitHub account. If you don’t see “Read the Docs” listed, then you might need to connect GitHub to your social accounts as noted above.
See also
GitHub doc on requesting access to your organization OAuth for step-by-step instructions.
GitHub App
Warning
Our GitHub App is currently in beta, see our blog post for more information.
We are in the process of migrating our GitHub OAuth application to a GitHub App. We have two GitHub Apps, one for each of our platforms:
Features
When using GitHub, Read the Docs uses a GitHub App to interact with your repositories. This has the following benefits over using an OAuth application:
More control over which repositories Read the Docs can access. You don’t need to grant access to all your repositories in order to create an account or connect a project to a single repository.
No need to create webhooks on your repositories. The GitHub App subscribes to all required events when you install it.
No need to create a deploy key on your repository (Read the Docs for Business only). The GitHub App can clone your private repositories using a temporal token.
If the original user who connected the repository to Read the Docs loses access to the project or repository, the GitHub App will still have access to the repository.
You can revoke access to the GitHub App at any time from your GitHub settings.
Never out of sync with changes on your repository. The GitHub App subscribes to all required events and will always keep your project up to date with your repository.
Adding a project from a repository
To add a project from a repository, you need to install the Read the Docs GitHub App and grant access to that repository.
Once you have installed the GitHub App, click on the Projects tab, and click on Add project, search for the repository you want to create a project for, and then follow the instructions from there.
Connect a repository to an existing project
In case you manually added a project on Read the Docs, or if you want to connect your project to a different repository, you need to install the Read the Docs GitHub App and grant access to the repository you want to connect.
Once you have installed the GitHub App, go the Settings page of the project, and select the repository you want to connect from the Connected repository dropdown.
Manually migrating a project
We recommend using the migration page to migrate your projects from the old OAuth application to the new GitHub App.
But in case you need to manually migrate a project, you can follow these steps:
Go to the Settings page of your Read the Docs project, and click on Integrations, and delete all the integrations that are listed there.
Go to the settings page of your GitHub repository, click on Webhooks, and delete all the webhooks with URLs that start with:
https://readthedocs.org/api/v2/webhook/<your-project-slug>orhttps://app.readthedocs.org/api/v2/webhook/<your-project-slug>for Read the Docs Community.https://readthedocs.com/api/v2/webhook/<your-project-slug>orhttps://app.readthedocs.com/api/v2/webhook/<your-project-slug>for Read the Docs Business.
For projects using Read the Docs Business, go to the settings page of your GitHub repository, click on Deploy keys, and delete the deploy with a title matching the format
support@readthedocs.com (<your-project-slug>).
Revoking access
Warning
If you revoke access to the GitHub App with any of the methods below, all projects linked to that repository will stop working, but the projects and its documentation will still be available. If you grant access to the repository again, you will need to manually connect your project to the repository.
You can revoke access to the Read the Docs GitHub App at any time from your GitHub settings.
There are three ways to revoke access to the Read the Docs GitHub App:
- Revoke access to one or more repositories:
Remove the repositories from the list of repositories that the GitHub App has access to.
- Suspend the GitHub App:
This will suspend the GitHub App and revoke access to all repositories. The installation and configuration will still be available, and you can re-enable the GitHub App at any time.
- Uninstall the GitHub App:
This will uninstall the GitHub App and revoke access to all repositories. The installation and configuration will be removed, and you will need to re-install the GitHub App and reconfigure it to use it again.
Security
When cloning private repositories (Read the Docs for Business only) Read the Docs creates an installation access token, which has read access to the contents permission, and it’s scoped to the repository to be cloned.
This token is valid for one hour and GitHub automatically grants read access to the metadata permission, which allows to query the repository collaborators, events, and other metadata. By default, Read the Docs doesn’t show this token during the build, but the token is available during the whole build process. Make sure to not print it in your build logs, and that only trusted users are able to trigger builds on your project.
Note
If your repository is public, Read the Docs will not create an installation access token.
Note
The build log page is publicly accessible only if your project and version to build are marked as public. See more in Privacy levels.
Troubleshooting
- Repository not found in the repository list
Make sure you have installed the corresponding GitHub App in your GitHub account or organization, and have granted access to the repository your project will be connected to.
If you still can’t see the repository in the list, you may need to wait a couple of minutes and refresh the page, or click on the “Refresh your repositories” button on the project creation page.
- Repository is in the list, but isn’t usable
Make sure you have admin access to the repository you are trying to use for your project. If you are using Read the Docs Community, make sure your project is public, or use Read the Docs for Business to create projects from private repositories.
If you still can’t use the repository for your project, you may need to wait a couple of minutes and refresh the page, or click on the “Refresh your repositories” button on the project creation page.